Ammonium Sulfate
Professional Supply Factory Price Multi Functional Pure Ammonium Sulfate for Agriculture
Product Name: Ammonium Sulfate
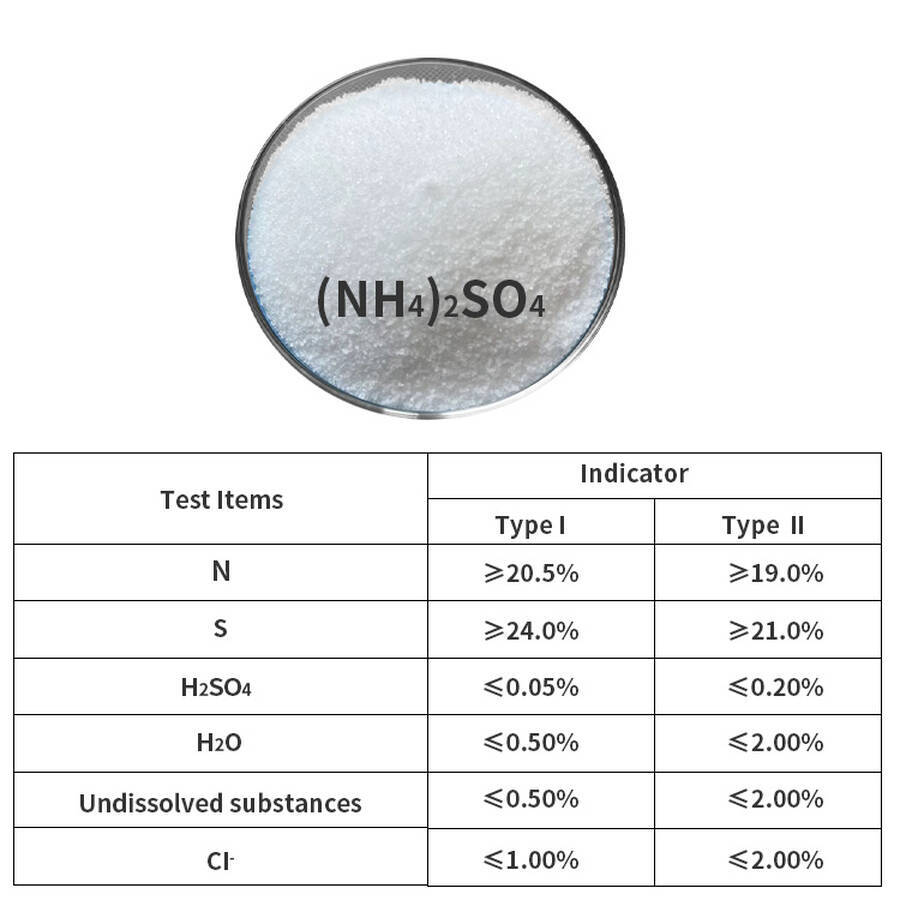
Assay: Nitrogen content ≥20.5%
CAS No.: 7783-20-2
EINECS No.: 231-984-1
Molecular Formula: (NH₄)₂SO₄
Molecular Weight: 132.14 g/mol
Hazardous Goods Code: None (Non-hazardous chemical under normal conditions, regulated as general cargo)
UN Number: None (Non-hazardous goods)
Packaging Specification: 50 kg/bag
Product Classification: By Source: By-product of coking By-product of caprolactam production By Form: Crystalline ammonium sulfate Granular ammonium sulfate Powdered ammonium sulfate
CERTIFICATES
Professional Supply Factory Price Multi Functional Pure Ammonium Sulfate for Agriculture
1. Appearance and Properties:
-
Pure Product: Colorless transparent rhombic crystals or white crystalline granules with no distinct odor.
2. Key Physical Parameters:
-
Relative Density (water = 1, 20°C): 1.77 g/cm³
-
Melting Point: 280°C (with decomposition; decomposes into ammonia, nitrogen, sulfur dioxide, and water above this temperature)
-
Solubility: Readily soluble in water with a solubility of approximately 75.4 g/100 mL at 20°C. The aqueous solution is weakly acidic (pH ≈ 5.5–6.0). Insoluble in ethanol, acetone, diethyl ether, and other organic solvents; slightly soluble in glycerol.
3. Chemical Stability:
Stable under normal temperature and pressure conditions. Exhibits no oxidizing or explosive properties. When heated with strong bases (e.g., sodium hydroxide), it releases ammonia gas (recognizable by its pungent odor). Reacts with barium salts such as barium chloride and barium nitrate to form a white precipitate of barium sulfate. Prolonged storage in a humid environment may lead to slow moisture absorption and caking, though the chemical composition remains unchanged.
4. Core Production Process
| Process Type | By-product Recovery Method |
| Raw Materials |
|
| Core Process Flow | Collection of by-products (solutions or slurries containing ammonium sulfate) → Purification (removal of tar, iron ions, organic impurities, etc.) → pH adjustment through neutralization (5.0-6.0) → Evaporation and concentration → Crystallization → Drying → Refinement → Final product |
| Product Characteristics |
|
5. Main Application Areas
5.1. Agricultural Sector (Core Application, >70% Share):
-
Nitrogen Fertilizer: Suitable for a wide range of crops including rice, wheat, corn, cotton, vegetables, and fruit trees. Particularly suited for acidic soils and sulfur-deficient soils. Supplies both nitrogen and sulfur nutrients, promoting darker green leaves, plump grains, and improving yield and quality.
-
Compound Fertilizer Blending: Serves as a key raw material for compound fertilizers and organic-inorganic compound fertilizers. Combined with elements like phosphorus and potassium to produce specialized fertilizers (e.g., specialized rice fertilizer, specialized vegetable fertilizer).
-
Feed Additive: High-purity agricultural-grade ammonium sulfate can be used in small quantities in ruminant feed to supplement non-protein nitrogen and promote rumen microbial growth (must comply with relevant feed-grade standards).
5.2. Industrial Sector:
-
Mineral Processing: Primarily used as a modifier and depressant. Its core functions are regulating the pulp environment and improving mineral floatability to aid the separation of target minerals from gangue. Specific uses include: 1. Acting as a pH modifier to optimize pulp alkalinity/acidity. 2. Acting as a depressant to inhibit the flotation of gangue minerals.
-
Chemical Synthesis: Used in the production of chemicals like ammonium persulfate and potassium sulfate. Also serves as a precipitating agent in the production of rare earth elements.
-
Textile Industry: Used as a mordant in fabric dyeing to improve dye adhesion. Acts as a dehydrating agent in silk scouring, improving silk luster.
-
Water Treatment: Used in industrial wastewater treatment as a coagulant aid to remove suspended solids. Can also be used in drinking water purification to adjust pH.
5.3. Other Sectors:
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: Used as an excipient in pharmaceuticals, serving as a crystallizing agent in the production of antibiotics, vitamins, etc.
-
Electronics Industry: High-purity ammonium sulfate is used for cleaning semiconductor materials, removing surface impurities.
-
Laboratory: Used as an analytical reagent, e.g., as a precipitating agent in quantitative analysis, a buffer component, or in culture medium preparation.
6. Safety and Protection Guidelines
6.1. Hazard Overview
-
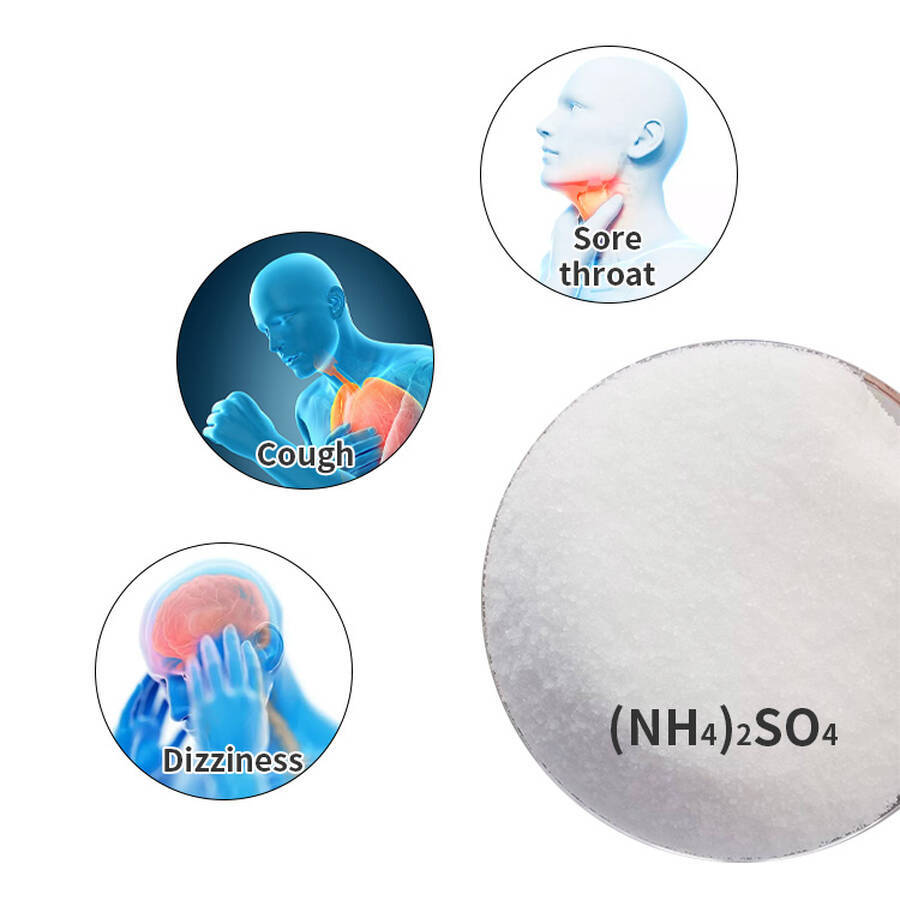
Health Hazards: Generally non-toxic upon normal contact. Inhalation of high concentrations of dust may irritate the respiratory tract, causing coughing and throat discomfort. Prolonged skin contact with dry powder may cause mild dryness but is non-corrosive. Ingestion of small amounts (non-food-grade) may cause mild gastrointestinal discomfort (e.g., bloating); seek medical attention for large ingestions (food-grade poses no risk when used according to standards). Decomposition products include ammonia gas, which is irritating; excessive inhalation can cause dizziness and nausea.
-
Environmental Hazards: Excessive agricultural application may lead to soil acidification and water eutrophication (due to nitrogen loss). However, it is readily absorbed by crops, exhibits no long-term cumulative toxicity in the natural environment, and is biodegradable.
-
Fire & Explosion Risk: Non-flammable, non-explosive. Upon exposure to open flame or high temperature, it only decomposes (releasing gases like ammonia), posing no fire or explosion hazard. No violent reaction when mixed with strong oxidizing agents.
6.2. Handling and Storage Requirements
-
Handling Instructions:
-
When handling powdered or granular products in dusty environments, wearing a dust mask (e.g., KN90) is recommended to avoid inhalation. Wash hands after contact. Maintain ventilation in the operating area.
-
For dissolution, slowly add ammonium sulfate to water with stirring until dissolved; no special temperature control is required (the dissolution process involves slight heat absorption, which is normal).
-
Avoid mixing or storing with strong alkalis (e.g., sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide) to prevent the release of irritating ammonia gas. Separate operations from barium salts to avoid the formation of toxic precipitates.
-
-
Storage Conditions:
-
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated warehouse. Temperature ≤ 30°C, relative humidity ≤ 75%. Protect against moisture to prevent caking (caked product can be crushed and used without affecting performance).
-
Packaged in polyethylene woven bags (with plastic liner) or paper bags. Net weights: 25kg/50kg/1000kg. Separate storage is required for agricultural-grade, industrial-grade, and food-grade products; mixing is strictly prohibited.
-
Keep away from strong alkalis, food raw materials, and pharmaceuticals. Regularly inspect packaging integrity in the storage area; replace damaged packages promptly to prevent leakage and moisture absorption.
-
6.3. Emergency Response Measures
-
Spill Response:
-
Small Spills: Collect powder/granules using a clean broom or shovel and place in sealed bags. The material can be used for agricultural fertilization (agricultural-grade) or industrial recycling (industrial-grade).
-
Large Spills: Cover with plastic sheeting to prevent dust dispersion or moisture absorption/caking. Collect gradually into corrosion-resistant containers. Dispose of via professional organizations. Prevent entry into sewers or rivers. If entry into a water body occurs, notify environmental authorities promptly.
-
-
First Aid Measures:
-
Skin Contact: Remove contaminated clothing. Rinse skin with flowing water for 1-2 minutes. No specific treatment is usually needed.
-
Eye Contact: Immediately open eyelids and rinse thoroughly with physiological saline or flowing water for 5-10 minutes. If discomfort persists, seek medical attention.
-
Inhalation: Move to fresh air. Keep the respiratory tract clear. If inhalation of ammonia gas causes dizziness or nausea, rest usually provides relief. Seek medical attention for severe symptoms.
-
Ingestion (Non-Food-Grade): Immediately drink plenty of warm water for dilution and expulsion. If vomiting or abdominal pain occurs, seek medical attention (no treatment needed for food-grade if ingested according to standards).
-
-
Fire Fighting Methods: The substance itself is non-combustible. No special firefighting measures are required. Focus on cooling surrounding containers to prevent packaging damage and product release due to heat. If a fire involves other combustible materials, use water, dry powder, or carbon dioxide extinguishers.
6.4. Transportation Requirements
-
Packaging must use plastic woven bags with tight seals to prevent leakage and moisture absorption/caking during transport. Food-grade product packaging must be marked with "Food Additive" and "Keep Dry" labels.
-
Vehicles do not require hazardous goods transport qualifications. Compartments must be kept dry and clean. Avoid mixed transport with damp goods or strong alkaline substances.
-
Protect from direct sunlight, rain, and high temperatures during transport. Handle with care during loading/unloading to prevent packaging damage.